special test for posterior tibialis tear|tibialis posterior arch support : dealer The single-leg heel raise was the most reliable of the 4 clinical tests for tibialis posterior tendinopathy (TPT). All tests had small to moderate associations with ultrasound grayscale changes. Clique Aqui para Acessar Resultados de Exames Laboratori.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Jogadores no plantel: 30. Média etária: 26,9. Estrangeiros: 9 30,0 %. Jogadores de Seleção: 8. Estádio: Prince Faisal bin Fahad Stadium .
Special tests for PTTD/AAFD include: The too many toes sign: the foot should be inspected from behind and above. The too many toes sign is a manner of inspection from behind. Clinical tests for tibialis posterior tendinopathy demonstrated moderate to substantial reliability, and small to moderate associations with ultrasound imaging findings. The single-leg heel raise was the test most . Stuart outlines all common objective tests you would expect to complete with suspected PTTD, but now we are looking through the lens of the Johnson and Strom classification system; for example, when looking at foot . The single-leg heel raise was the most reliable of the 4 clinical tests for tibialis posterior tendinopathy (TPT). All tests had small to moderate associations with ultrasound grayscale changes.
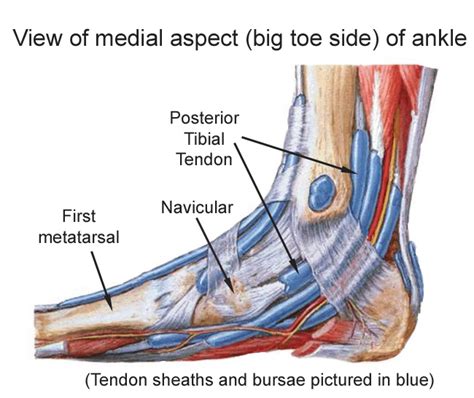
Posterior Tibial Tendon Insufficiency is the most common cause of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity, caused by attenuation and tenosynovitis of the posterior tibial tendon leading to medial arch collapse. A single-limb heel rise test can also determine the health of your posterior tibial tendon. For this test, you’ll stand next to a wall or chair to support your balance. Then you’ll .The posterior tibial tendon (PTT). The PTT attaches one of the calf muscles (the tibialis posterior muscle) to the bones on the inside arch of the foot. You may be able to see or feel this tendon as it runs behind the inside bump of your ankle . Diagnosis may be confirmed with an MRI scan or ultrasound. Treatment for tibialis posterior tendon rupture. All patients who potentially have a tibialis posterior tendon rupture should see a physiotherapist or doctor .
Abnormal findings on ultrasound that can be seen in posterior tibialis tendinopathy include fluid within the tendon sheath, thickening of the tendon or tendon sheath, . Tibialis posterior tendonitis (also known as posterior tibial tendonitis) is, in my experience, one of the trickier tendon injuries to treat. This article explains what causes tibialis posterior tendonitis, how to figure out . Posterior tibial tendonitis can cause pain and adult acquired flatfoot deformity. Early, noninvasive treatments can help before surgery is needed. . However, some will have had no recent injury. The tendon can .Injury to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) can range from a stretch to a total tear or rupture of the ligament. . Special tests [edit | edit source] Posterior drawer: . The posterior tibial sublaxation caused by the hamstring is .
tibialis posterior tendon sheath
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the strongest and largest intra-articular ligament in human knee and the primary posterior stabilizer of the knee. It comprises of 2 functional bundles: the larger anterolateral bundle (ALB) and the smaller posteromedial bundle (PMB). The size of the femoral attachment of the ALB is nearly twice the size of its tibial attachment[1].
The Tibialis Posterior is located deep in the posterior compartment of the lower leg and situated between the Flexor Digitorium Longus and the Flexor Hallucis Longus.It is a key stabilising muscle supporting the medial arch of the foot.. Origin [edit | edit source]. The origin of the muscle is: . Proximal postero-lateral aspect of the tibia. Proximal postero-medial aspect of the fibula .An adjunct to the clinical special tests in assessing anterior translation is the use of instrumented laxity testing. The most commonly cited arthrometer is the KT1000 (Medmetric, San Diego, California). The arthrometer provides an objective measurement of the anterior translation of the tibia that supplements the Lachman test in ACL injury.
Orthopedic Exam / Special Tests for Physical Therapy: KNEE McMurray’s Test. Meniscal injuries may be the most common knee injury. Meniscus tears are sometimes related to trauma, but significant trauma is not necessary. A sudden twist or repeated squatting can tear the meniscus. A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. Any activityMedial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS) is a common overuse injury of the lower extremity. It typically occurs in runners and other athletes that are exposed to intensive weight-bearing activities such as jumpers.It presents as exercise-induced pain over the anterior tibia and is an early stress injury in the continuum of tibial stress fractures.. It has the layman's moniker of .Tarsal tunnel syndrome (TTS) is a compressive neuropathy of the posterior tibial nerve. The tunnel lies posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle, beneath the flexor retinaculum. . Special Tests: Tinel’s Sign: . The important finding on electromyography (EMG) is the demonstration of axonal injury when the EMG is recorded from the .The medial collateral ligament is a big ligament on the medial side of the knee. For more clinically relevant anatomy of the knee click here.The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of the four ligaments that are critical to maintaining the mechanical stability of the knee joint. The ligamentous sleeve spans the entire medial side of the knee from the medial aspect of the .
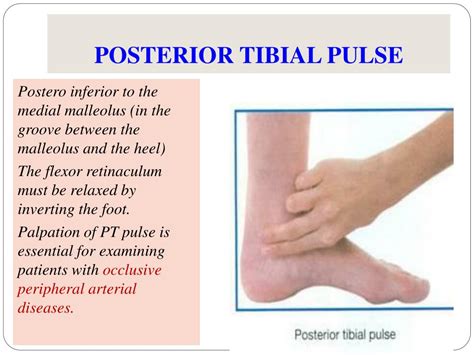
tibialis posterior palpation
Tibial stress syndrome (also known as shin splints) is an overuse injury or repetitive-load injury of the shin area that leads to persistent dull anterior leg pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with tenderness along the posteromedial distal .
The Lachman test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament in a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test is used to evaluate the anterior translation of the tibia in relation to the femur and is considered a variant of the anterior drawer test. Multiple studies have shown that the Lachman test is the .Diagnosis of Posterior Tibialis Tendon Tear. Your physician may be able to diagnose you by performing an exam and considering the signs and symptoms. Some imaging may be ordered, such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI, to rule out other .
shampoo bottle test
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. Medial meniscus tears are generally seen more frequently than tears of the lateral meniscus, with a ratio of approximately 2:1. Meniscal tears may occur in acute knee injuries in younger patients or as part of a degenerative process in older individuals. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a traumatic knee effusion and increased laxity on a posterior drawer test but requires an MRI for confirmation. . asymmetric posterior tibial displacement indicates PCL .
Objective: To determine the reliability of common clinical tests for tibialis posterior tendinopathy (TPT) and to investigate their relationship with grayscale ultrasound findings in individuals who have medial foot/ankle pain. Design: Prospective cohort. Methods: Fifty-two individuals reporting medial foot/ankle pain were clinically examined by 2 physical therapists using 4 clinical tests .What causes posterior tibial tendonitis or tears? Posterior tibial tendon problems can occur for a variety of reasons, including: Overuse: Overuse symptoms occur after activities that use the tendon, such as walking, hiking or climbing stairs, especially when a . docking into the tibial tunnel posterior to anterior with graft #2 graft #2 reconstructs the popliteus tendon proximal attachment site at the anatomic popliteus tendon attachment
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), now renamed progressive collapsing foot deformity (PCFD), is the most common cause of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Failure of the posterior tibial tendon (PTT) affects surrounding ligamentous structures and eventually leads to bony involvement and deformity. PTTD is a progressive and debilitating .Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition that leads to inflammation or a tear in this tendon. When the tendon is damaged, it can no longer support the arch.The treatment plan for posterior tibial tendon tears varies depending on the flexibility of the foot. The treatment for a foot where there is no motion or motion is limited is different than treatment for a flexible foot. . Imaging Tests. Other tests which may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. X-rays provide detailed .
tibialis posterior muscle action
Plantar fasciitis (Currently better referred to as Plantar Heel Pain) is the result of collagen degeneration of the plantar fascia at the origin, the calcaneal tuberosity of the heel as well as the surrounding perifascial structures. It is also called Plantar Fasciopathy (reflecting the absence of inflammation). The plantar fascia plays an important role in the normal biomechanics of the foot. Grade I tears of the tibialis anterior tendon typically do not require surgery. After a few weeks of immobilization, you can begin rehabbing the injury. A grade II rupture may need a few more weeks of rest, after which time you can start physical therapy (PT) to safely regain mobility of your foot and ankle.; A full-thickness grade III rupture of your tibialis anterior .
Introduction [edit | edit source]. The menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures that function to deepen the tibial plateau, improve articulation of the femur on the tibia, stabilize the knee, and assist with shock absorption. The medial meniscus specifically forms almost a semicircular shape and covers 50-60% of the articular surface between the medial femoral condyle and the medial .Posterior tibialis tendon surgery is a way to fix the tendon on the back of your calf that goes down the inside part of your ankle. . provider might be more likely to advise surgery right away if you hurt your posterior tibialis tendon very badly or if the injury happened suddenly. . you may need imaging tests such as an X-ray or magnetic .Conservative management of PTTD. Once you’re confident in your diagnosis of PTTD, treatment will include a combination of all your usual suspects – education, load management, ice/anti-inflammatories, taping, orthotics/heel lifts, calf/dorsiflexion mobility and strengthening the tibialis posterior as well as the other structures supporting the medial longitudinal arch.The Tibialis anterior (Tibialis anticus) is situated on the lateral side of the tibia; it is thick and fleshy above, tendinous below. The fibers run vertically downward, and end in a tendon, which is apparent on the anterior surface of the muscle at the lower third of the leg. This muscle overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal .
tibialis posterior lengthening
tibialis posterior arch support
right posterior tibial tendon
Resultado da So I was curious and from a playthrough that I watched the gym/ e4 battles of moon black 2 are as follows: 15, 20, 27, 36, 42, 49, 56, 62 Elite four are all 72 with aces of 74 Champ has 73 -75 Reply reply embernheart • • Edited .
special test for posterior tibialis tear|tibialis posterior arch support